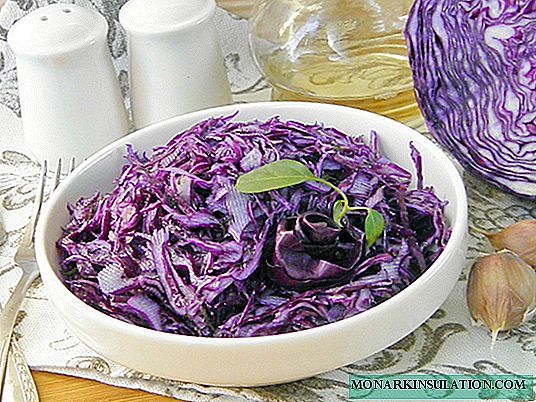
Red cabbage is a very close "relative" to all familiar white cabbage. In addition to the unusual shade of leaves, there are several more differences between them, but agricultural technology has practically no nuances. Care is no more difficult than for ordinary cabbage, nothing supernatural from the gardener is required. Recently, a lot of varieties and hybrids bred by breeding have appeared, devoid of a specific bitter taste, which until then had prevented the culture from gaining wide popularity.
What does red cabbage look like and how it is useful
Based on the botanical description, red cabbage is practically no different from the usual white cabbage. The unusual shade of the leaves is due to the presence of anthocyanins. It can vary from purple to red-violet and blue-lilac. The type of soil also affects it. In acidic soil the leaves turn red, in alkaline soil they turn blue. Anthocyanins give red cabbage a specific island-bitter aftertaste that not everyone likes. But most modern varieties and hybrids bred by breeders lack this unpleasant feature.
Our country has been familiar with this culture for a long time. The first mention of red cabbage was found at the end of the 18th century. Its historical homeland is the Mediterranean. This cabbage is especially common in Turkey, Greece, Tunisia, Algeria.

In popularity among Russian gardeners, red cabbage is much inferior to white cabbage
The average weight of a head of cabbage varies from 1-1.2 kg to 3.5-4 kg. It depends on the variety. In shape, they can be almost round and flattened, domed ones are somewhat less common. The stem of the plant is very short, heads of cabbage almost lie on the ground. The root system is powerful, developed. Due to this, red cabbage tolerates drought well and rarely leaves the arrow.

The vegetative period of red cabbage is long, it often remains in the garden until frost
Practice shows that red cabbage is more hardy than white cabbage, less likely to suffer from diseases and pests, and forms very dense heads of cabbage. The optimum temperature for the development of culture is 16-18ºС. Recently transplanted seedlings in the garden can make it drop to -4-6 ° C, adult plants - to -6-8 ° C.

Red cabbage heads are very dense
The leaves are not juicy, so red cabbage is not suitable for pickling. The color of the dishes during the heat treatment is specific, in addition, a significant part of the benefits in the process is lost. But in salads, this cabbage is very good. It can also be salted and pickled. And if you prepare a side dish for a meat dish, heavy food is better and faster to digest.

In Russia, red cabbage is rarely pickled, but in Europe it has long been appreciated
Harvest is usually harvested 2-3 weeks after the cabbage. But there are also some exceptions - varieties bred by breeders in which heads are formed in 100 days or less. Also, this cabbage is appreciated for portability and keeping quality. Almost any of its varieties due to the density of heads of cabbage is stored no worse than the later varieties of white cabbage specially designed for this purpose. In the cellar, basement, another dark place with good ventilation, humidity 80% and above, temperature 0-4ºС, it can lie all winter without losing the presentability of appearance, taste and benefits.
Red cabbage is extremely beneficial for health:
- vitamin C in it is twice as much as in white. You can also note the presence of vitamins of group B, A, K, E, PP, U, iron, sodium, phosphorus, potassium, zinc, magnesium, selenium, copper;
- anthocyanins that affect the color of leaves strengthen the walls of blood vessels, restore elasticity to them, reducing the risk of suffering from a heart attack and stroke;
- volatile drugs have a pronounced antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effect;
- glucosinolates are natural anticarcinogens. They can affect uncontrolled cell division. It is scientifically proven that with regular use of this vegetable, the risk of developing breast cancer in women is halved;
- red cabbage is rich in proteins (it may well replace meat for vegetarians) and amino acids. These substances are necessary for the normal functioning of the thyroid gland, kidneys, and liver. Without lactic acid, the proper functioning of the muscles, heart and brain is impossible;
- fiber helps cleanse the intestines of toxins and toxins, normalize its microflora;
- red cabbage lacks sucrose and starch. This means that the vegetable can be eaten even in the presence of diabetes of any type and can be safely included in the diet for those who want to lose weight. Its calorie content is only 25-26 kcal per 100 g;
- useful and the juice of this cabbage. Due to its wound healing and anti-inflammatory effects, it is used to treat gastritis, stomach and intestinal ulcers, as well as tonsillitis, stomatitis, periodontal disease. And if you add honey, the juice helps with bronchial asthma, tuberculosis, bronchitis. With regular use, tooth enamel and nail plates are strengthened, complexion and skin tone improve, hair becomes softer and less likely to break. The daily norm of juice is no more than a glass. It can be mixed with carrot, but can not be salted and filtered.

Red cabbage juice is very good for health, it is also used as a natural dye
Since ancient times, red cabbage has been known to neutralize the effects of alcohol on the body, helping to maintain clarity of mind. This tool was used in the Roman Empire. It is enough to drink half a glass of juice before a feast or eat a portion of salad. The same measure alleviates or neutralizes the state of a hangover the next morning.

Fresh red cabbage or its juice helps to neutralize the negative effects of alcohol
There are contraindications. With excessive consumption, red cabbage can cause problems with the stomach, which is not able to quickly digest large amounts of fiber. This leads to bloating, flatulence. The development of iodine deficiency is also possible - red cabbage provokes the absorption of this trace element by the body in large quantities. This vegetable is strictly prohibited in pancreatitis, enterocolitis, other diseases of the stomach, intestines and kidneys in the acute stage.
Nutritionists recommend including red cabbage in the diet for anyone living in adverse environmental conditions. It also helps the body minimize the effects of secondhand smoke and reduce the negative impact of ultraviolet and electromagnetic radiation on it.
Video: the benefits of red cabbage
Common varieties
Red cabbage is not as popular with breeders as white cabbage, but still there are quite a few varieties and hybrids that differ in shade of leaves, yield, and shape of heads of cabbage. The frost resistance of most of them allows you to grow red cabbage not only in central Russia, but also in the Urals and Siberia. Heads of cabbage manage to form, despite the long vegetative period.
The most popular varieties:
- Mikhnevskaya. The variety was bred back in the late 60s of the last century. The taste is not bad, but not outstanding. It has good immunity against fungal diseases, rarely is attacked by harmful insects;
- Mars MS. Variety of Czech selection. The growing season is 105-110 days. Valued for its high yield. Heads weighing 1.3-1.5 kg practically do not crack. The density is average. Outside, heads of cabbage are black-violet, much lighter on the cut. Cabbage of this variety is intended mainly for fresh consumption;
- Approximately F1. Early hybrid from the Netherlands. It is distinguished by taste (not bitter) and a presentable appearance. The socket is compact, the leaves are small, ink-violet, almost black, covered with a bluish-blue wax coating. Heads of cabbage are almost round, dense, one-dimensional, weigh 3-4 kg, and do not crack. The hybrid gives high yields, even when thickening plantings;
- Romanov F1. The plant is quite compact. Heads are spherical, dense, weigh an average of 1.5-2 kg. The leaves are deep red with purple tint. Shelf life is small - 2-3 months;
- Kyoto F1. A Japanese high-yielding hybrid with genetically integrated immunity to most culture-specific diseases. The plant is compact, the average weight of the head is about 1.5 kg, the stalk is practically absent. The taste is excellent, the leaves are quite tender. Heads of cabbage rarely crack, stored for 4-5 months;
- Garancy F1. The hybrid is from France. The growing season is 140-145 days. It is stored until next spring. Valued for high yield, disease resistance, resistance to cracking. It is desirable to grow this cabbage in greenhouses or under film shelter. Heads weighing about 3 kg are dense. The taste is sweet, without pungency and bitterness;
- Benefit F1. Achievement of Russian breeders. Cabbage is very fresh. It features a vertical rosette of leaves. Heads of cabbage weighing about 1.5 kg or a little more. It has an "innate" immunity to Fusarium. Leaves are blue with a greenish tint;
- Pallet. The growing season is 140-150 days. The variety is ideal for long-term storage, but good and fresh. Heads of cabbage are round, very dense, weighing 1.9-2.4 kg. The variety stably bears fruit, even if the weather in summer is not very successful;
- Nurima F1. Another popular Dutch hybrid. The plant is compact, the weight of spherical heads of cabbage varies from 1 to 2 kg. It is advisable to plant this cabbage under cover material;
- Juno. Russian grade. The growing season is 130-140 days. The leaves are dark purple with a thick waxy coating. Heads of cabbage are round, weighing about 1 kg or a little more. Appreciated for its wonderful taste, it is mainly consumed fresh. Productivity - about 4 kg / m²;
- Rodima F1. Dutch hybrid. Heads of cabbage are almost round, maroon, weighing 3 kg or more, do not crack. The leaves are large, covered with a thick layer of bluish plaque. The growing season is 140-145 days. The variety is distinguished by its versatility, ideal for the preparation of salads. The crop is stored until the middle of next summer. The taste is delicate, very intense. When grown under cover material or film, productivity increases significantly;
- Gako 741. Time-tested variety, grown since the 40s of the twentieth century. It is very well stored (at least until the beginning of next spring) and transported. It is also appreciated for its high cold and drought tolerance. Very rarely suffers from diseases and pests. Heads of cabbage are dark violet, do not crack. Average weight - 1.5-2 kg, individual specimens reach 3 kg;
- Vanguard F1. A variety of medium ripening. The socket is powerful, vertical. The leaves are large, purple, covered with a thick layer of bluish plaque, not very corrugated. Heads are flattened, dense, weighing a little over 2 kg. The variety is immune to fusarium;
- Autoro F1. Dutch hybrid. The growing season is 135-140 days. Differs in high productivity. Heads of cabbage are very dense, burgundy. The average weight is 1.2-1.5 kg. They practically do not crack. The hybrid is often affected by the keel;
- Boxer. One of the earliest varieties, intended primarily for fresh consumption. Heads are spherical, weighing approximately 1.5 kg or slightly more. The leaves are red-violet, with a slight silver coating;
- Intro F1. The socket is powerful, slightly raised. Dark violet leaves are almost completely covered with a bluish-blue coating. The surface of the sheet is uneven, inside as if a lot of small bubbles. The head of cabbage is quite loose, weighs about 2 kg;
- Calibos. The growing season is 140-150 days. A variety with good frost resistance, tolerates sudden changes in temperature and excess moisture. Heads are domed, reddish-violet, medium in size (weighing about 1.5-2 kg), not too dense. The leaves are tender, juicy, cabbage has a sweet taste. When cultivating this variety, special attention should be paid to watering. It is recommended for fresh consumption, can be stored for about 4 months;
- Stone head 447. "Honored" Soviet grade. The term for heading out is 125-145 days. The outlet is sprawling, with a diameter of 80 cm or more. Heads are almost round, dense, weigh about 1.5 kg. Ripen at different times, often crack. The leaves are reddish with purple tint. Average productivity, shelf life - until mid-winter;
- Lyudmila F1. A variety from the early ripening category, cabbage is intended mainly for fresh consumption. The leaves are medium-sized, almost round, greenish-purple with a thick bluish bloom. The edges are highly corrugated. Taste is excellent. The average weight of a round or slightly flattened head of cabbage is 1.8-2 kg;
- Maxilla. Heads of cabbage differ in good keeping quality, are stored until the beginning of next spring. Immediately eating them is not recommended: the leaves are rough. But during storage, they become more tender, and taste is improved. It is advisable to let the cabbage lie down at least before the start of winter;
- Rubin MS. A popular high-yielding Czech variety. From planting seedlings to ripeness - 120-130 days. Heads of flattened shape, dark purple, very dense. Weight varies from 1 kg to 2 kg. This cabbage can be stored until mid-winter, but is good and fresh.
Photo gallery: varieties of red cabbage, popular among Russian gardeners

- Cabbage Mikhnevskaya is valued mainly for keeping quality and transportability.

- Cabbage Mars MS - a high-yielding variety with not too dense heads of cabbage

- Cabbage Primero F1 - the Dutch hybrid popular around the world

- Cabbage Romanov F1 has compact enough sockets to help save space on the bed

- Kyoto F1 cabbage has practically no cob

- Garancy F1 cabbage is practically devoid of flaws, but you need to grow it in a greenhouse or at least under a film

- Cabbage Benefis F1 never suffers from Fusarium

- Cabbage Pallet is suitable for fresh consumption, and for long-term storage

- Nurima cabbage F1 has one-dimensional beautiful heads of cabbage

- Juno cabbage ripens late

- Rodima F1 cabbage stands out for its large head size
- Gako Cabbage 741 has the ability to adapt to adverse weather factors

- Cabbage Vanguard F1 powerful spreading rosettes of leaves

- A significant drawback of Autoro F1 cabbage is its tendency to get infected with keel

- Cabbage Boxer ripens one of the first, not suitable for long-term storage

- Hybrid Intro F1 leaf texture is easy to confuse with Savoy cabbage

- Calibos cabbage is very easy to identify thanks to its irregular shape

- The name of the cabbage Stone head 447 speaks of the extraordinary density of heads of cabbage

- Hybrid cabbage Lyudmila F1 is distinguished by excellent taste

- The taste of cabbage Maxilla significantly improved during storage
- The weight of heads of cabbage Rubin MS varies greatly
Growing seedlings and caring for them
Since the vast majority of varieties and hybrids of red cabbage are characterized by a long vegetative period, they are most often grown with seedlings. Planting seeds directly into the soil is possible only in the southern regions, but it is rarely practiced there because of their high consumption and the need for careful care of seedlings.
Preplant seed preparation is required. First, they are dipped for 15-20 minutes in hot (45-50 ° C) water, then for 2-3 hours - in cold.After this, the seeds are pickled for 24 hours in a pale pink solution of potassium permanganate or any fungicide of biological origin (Ridomil Gold, Fitosporin, Baikal-EM, Bayleton). This is necessary for the disinfection and prevention of fungal diseases. In the second case, the processing time is reduced to 25-30 minutes. The last thing to do before planting is to rinse the seeds in cool running water and dry them. The best time to land is mid-March.
Seedlings are grown as follows:
- Shallow flat containers are filled with a mixture of peat chips and fertile turf. The substrate must first be disinfected.

The soil for planting red cabbage seeds must be disinfected by steaming, heat or freezing
- Seeds are sown with an interval of 2-3 cm, deepening no more than 1 cm. The distance between the rows is 3-4 cm. They are sprinkled with fine sand on top and moisten the soil from a finely dispersed atomizer. The container is covered with glass or a transparent film. Until germination, it is kept in a dark place. The optimum temperature is 16-20ºС. In this case, the first sprouts appear after 2-3 days. Until the seeds hatch, the soil is not watered.

The film or glass is removed from the tank daily to get rid of accumulated condensate.
- After the emergence of sprouts, the containers are transferred to the brightest place in the apartment, the shelter is removed. For the proper development of red cabbage, daylight hours of at least 14 hours are required, therefore, additional exposure may be required. For this, ordinary luminescent or special phytolamps are used. For the first 7-8 days, the temperature is lowered to 8-10 ° C, then it is again raised to 12-16 ° C and maintained, without changing, until it lands in the ground.

For normal development, sprouts of cabbage need a long daylight
- Red cabbage is hygrophilous. Seedlings are often but moderately sprayed. Like any cabbage, it is prone to become infected with a "black leg", so every 7-10 days, water for irrigation is replaced with a pale pink solution of potassium permanganate. They feed seedlings twice - when 2-3 real leaves are formed and about a week before transplanting into the garden. 3 g of simple superphosphate and 2 g of urea and potassium sulfate are taken per 1 liter of water. Any complex fertilizer for seedlings is also suitable.

Fertilizer Rostock - a comprehensive tool designed to feed seedlings
- Diving is carried out in the phase of the second real sheet. Seedlings are planted in small individual containers, pinching the root. Then the cabbage should be moderately watered and covered for 3-5 days from direct sunlight. If you use peat pots, then seedlings from them before planting in the ground will not have to be removed.

In the process of diving, pinch the root of the seedling of cabbage
- A couple of weeks before planting, seedlings begin to harden. The first 2-3 days just open the window in the room for several hours, then the containers are taken out to the glassed-in balcony or loggia during the day. The last 3-4 days before landing, they remain on the street. At the same time, they are sprayed with a solution of any biostimulant (Epin, Zircon, Heteroauxin, potassium humate are suitable).

Hardening the seedlings of cabbage helps her adapt to new living conditions
Video: how to care for cabbage seedlings
Landing cabbage in the ground
In the garden, you can plant seedlings of red cabbage at the age of 35-45 days. Such plants reach a height of 16-20 cm and have at least 4-5 true leaves. To make it easier to remove from the tank without damaging the roots, about half an hour before the procedure, the earth should be abundantly watered. Red cabbage is planted in the ground in early May, choosing a dry, cool day for this.

With the planting of red cabbage seedlings in the soil, you should not hesitate, overgrown seedlings poorly take root
The plant categorically does not tolerate stagnation of moisture at the roots. Therefore, the soil should be light enough, well permeable to water and air, but at the same time nutritious. The acid-base balance is neutral (pH 5.5-7.0). You can not plant red cabbage in the lowlands or where groundwater comes closer to the surface by more than 1.5 m. If there is no other place, you will have to build ridges at least 60 cm high.
When choosing a place for a bed, you need to take into account that in penumbra and shade, heads of cabbage acquire an uncharacteristic greenish tint, become loose, and mature longer than usual.

Red cabbage must be planted in an open place, even light penumbra does not fit it
Good precursors for the plant are any solanaceous, bean, onion, garlic, spicy herbs, beets, carrots. After other varieties of cabbage, it is planted in the same place only after 4-5 years. Otherwise, keel infection is almost inevitable.
Since the autumn, the soil has been carefully dug up and humus or rotted compost added to increase soil fertility. If there is no organics, use any complex nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium fertilizers (Azofoska, Diammofoska). Dolomite flour, sifted wood ash, and powdered eggshell are additionally added to acidic soil.
When planting in the ground, excessive thickening of the plantings is avoided by placing holes with an interval of at least 60 cm. The distance between the rows of landings is about 70 cm. About half an hour before the procedure, the wells are shed with water. In each put a handful of humus, 1 tsp. potassium fertilizer without chlorine, 2-3 pinches of crushed chalk or sifted wood ash and a little onion husk.

When planting seedlings of red cabbage in the ground, it is important to maintain the intervals between plants so that each of them gets enough space for nutrition
Seedlings are planted, deepening to a couple of cotyledon leaves. The soil around the plant is carefully compacted, cabbage is plentifully (about 2 liters of water) watered. For the first 10-12 days, it must be protected from direct sunlight. The easiest way is to build a temporary canopy over it from any covering material of white color.

Cabbage seedlings planted in the ground are abundantly watered
If the seeds are planted immediately in the garden, the soil is prepared in the same way. The landing pattern is also respected. The exact time may vary by region. In the southern subtropical climate, seeds can be planted already in early April, in central Russia - in the last decade of April, in the Urals and Siberia - in the first half of May.
3-4 seeds are placed in each hole, deepening them by 3-5 cm. Before seedlings appear, the garden bed is closed with plastic wrap or covering material on the arches. Then you need to carefully monitor the temperature in the street. If it exceeds 25ºС, the plants are stretched, the stems are deformed and bent.
When 2-3 real leaves are formed on the cabbage, the seedlings are thinned out, leaving in each hole one, the most powerful and developed seedling. The rest are carefully cut with sharp scissors so as not to damage the root system of the others. Seedlings are watered every 2-3 days, in moderation. To prevent the development of the "black leg" a week after the emergence of seedlings, the bed is dusted with crushed chalk or tobacco chips.
Crop care
Red cabbage is not particularly capricious and demanding to leave, although for some reason a different opinion has taken root among gardeners.
Watering
Red cabbage is a moisture-loving plant. Although it tolerates drought well, water scarcity negatively affects yield and quality of heads of cabbage. Frequent and plentiful watering is contraindicated in it - with stagnation of water at the roots, rot quickly develops. Therefore, the upper layer of soil must be allowed to dry.
Sprinkle cabbage under the root, if possible - then by sprinkling. She especially needs moisture when rosettes of leaves form, closing in a continuous carpet, and during the ripening of heads of cabbage.

Red cabbage is watered so that drops of water fall on the leaves, as in rain
The procedure is preferably carried out in the evening. If the weather is cool and cloudy, once every 4-5 days is enough. In the heat, the intervals between watering are reduced to 1-3 days. For seedlings, the norm is 2-3 liters per plant, during the formation of heads of cabbage, it increases to 4-5 liters. Mulch will help retain moisture in the soil.
It is categorically impossible to alternate a long “drought” with sparse, plentiful watering. This will almost inevitably lead to cracking heads.
Loosening
Loosen the bed often. The first time - 7-10 days after transplanting seedlings into the ground. Then the procedure is carried out every 3-4 days. When the seedlings take root in a new place and actively start to grow, they spud cabbage, filling the stem with soil until the first pair of true leaves. Ideally, the soil should be loosened after each watering until the moment when the leaves completely cover the soil. First, to a depth of 5-8 cm, 1-1.5 months after transplantation - by 12-15 cm.

Thanks to hilling, cabbage forms a powerful root system
In most varieties, the vegetative period is long, therefore, for a season of red cabbage, a minimum of 3-4 dressings is required. First, emphasis should be placed on nitrogen-containing fertilizers, helping the plant to intensively build green mass. This macronutrient is completely eliminated when heads of cabbage begin to form.
Excess nitrogen reduces the immunity of the plant, promotes the accumulation of nitrates in heads of cabbage, reduces their keeping quality and provokes the development of necrosis.
Feeding scheme:
- The first time red cabbage is fed 12-15 days after planting. For 1 m² take 10 g of carbamide, 15 g of potassium sulfate and 20 g of simple superphosphate. Fertilizers are poured into the grooves between the plants, then the grooves are buried, the garden is well watered.

Urea, like other nitrogen-containing fertilizers, helps cabbage to actively build green mass
- The second top dressing is carried out when the heads of cabbage begin to be tied up, approximately 2-3 weeks after the first. The fertilizer rate is increased by 1.5 times. You can use organics - water infused with cow manure, bird droppings, nettle leaves or dandelion.

Nettle infusion - a natural source of nitrogen and other macronutrients
- The third and subsequent feeding, carried out with an interval of 15-20 days, contain only phosphorus and potassium. They are brought in dry form (20-25 g / m²) or in the form of a solution, diluting the same amount in 10 l of water. You can alternate them with infusion of wood ash and complex fertilizers for cabbage without nitrogen.
Video: nuances of agricultural technology of red cabbage
Diseases and pests: control and prevention
Red cabbage suffers from diseases and pests much less frequently than white cabbage. But she is not immune from infection with keel, bacteriosis and fusarium. Of the pests, cabbage moth, caterpillars of the butterfly cabbage and cabbage scoops, aphids, and thrips cause the most harm to plantings.
In any case, the best prevention is competent crop care. No less important is crop rotation - spores of pathogenic fungi, eggs and larvae of pests gradually accumulate in the soil. With excessive thickening of plantings, any disease spreads much faster.

Fusarium disease is a very common disease that causes cabbage to die in a matter of days.
For the prevention of fungal diseases, preplant seed dressing of red cabbage in a fungicide solution is mandatory. After planting on the bed, the soil is sprinkled with crushed chalk or tobacco chips, the grown plants are dusted with wood ash. Every 12-15 days for prevention, the cabbage is sprayed with infusion of onion or garlic shooters, a bright pink solution of potassium permanganate or diluted with water kefir or serum with the addition of iodine (drop per 1 liter).
If infection could not be avoided, use any fungicides. As a rule, 3-4 treatments with an interval of 5-7 days are sufficient. Both old time-tested products (Bordeaux liquid, vitriol) are used, as well as modern copper-containing preparations - Topaz, Horus, Skor, Kuprozan.

Bordeaux liquid can be purchased at the store or prepared independently
The most dangerous disease for any cabbage is keel. The fungus very quickly infects the root system of the plant. The only way to deal with it is to observe crop rotation by planting red cabbage after crops that help to destroy fungal spores (solanaceous, beets, onions, garlic). It is equally important to regularly weed the garden.

It is impossible to get rid of the keel with modern means, so special attention should be paid to disease prevention
In order to avoid pest attacks, in early spring the soil on the bed is shed with Fufanon, Alatar, Tiovit Jet or boiling water. Most insects do not tolerate pungent odors. Therefore, planting cabbage is useful to surround the "barrier" of onions, garlic, herbs, marigolds, marigold, lavender. Against any butterflies, special pheromone or home-made traps in the form of containers filled with water diluted with water, honey, jam, sugar syrup are effective. You can also use drugs Lepidocide, Bitoxibacillin.

Aphid is one of the dangerous garden pests, it will not disdain any cabbage either
If there are not too many insects, folk remedies will help to cope with them. Cabbage can be treated with foam of green potash or laundry soap, infusion of hot pepper or tobacco, diluted in water with soda ash or colloidal sulfur. In the event of a mass invasion, any general insecticides are used - Inta-Vir, Iskra-Bio, Mospilan, Tanrek, Confidor-Maxi.
Harvesting and storage
Hurry up with the harvest is not worth it. Red cabbage is frost-resistant, so you need to focus exclusively on the size of the head of cabbage, typical for the variety. Most varieties can be removed in the second decade of October.
Heads intended for long storage are surely dug in dry cool weather, but at a plus temperature. They need to be carefully examined - there should not be even small cracks and the smallest traces of damage by diseases and insects.
Then they are allowed to dry for 2-3 days, after which the integumentary leaves are cut off with the exception of three or four and the root, leaving a 3-4 cm long stalk. The slices are immediately sprinkled with wood ash or crushed chalk.

Red cabbage, intended for long-term storage, is first carefully examined
Store crops in a garage, cellar, basement. The place must be dark and with good ventilation. The optimum temperature is 0-4ºС, air humidity is 80% and higher. Heads of cabbage are stacked in wooden boxes or cardboard boxes, sprinkled with sand so that they do not touch each other. You can still wrap each in paper and lay them on shelves, tie in pairs for stitches and hang them under the ceiling.
Video: how to keep cabbage harvest for a long time
Even a gardener who does not have much experience can cope with the cultivation of red cabbage. Contrary to popular belief, this culture is not too capricious and demanding to care for. Many varieties allow you to choose the most suitable, focusing on taste, productivity, appearance of heads of cabbage. The frost resistance of this variety of cabbage allows you to grow it in most of the territory of Russia.








































